Q1. What is Network Topology and its types?
Network Topology is the structure to organize and interconnect computers on a network . Different types of network topologies are:
i. Bus Topology
Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to single cable.
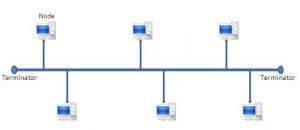
Advantages
- Short cable length.
- It is cost effective.
- It is easy to add new node.
Disadvantages
- It is difficult to find and correct errors on network.
- Only one computer transmits at a time.
- If one computer is dead, it will make entire network dead.
ii. Star Topology
In star toplogy all the computers are connected to a single hub. This hub is the central node and all others nodes are connected to the central node.
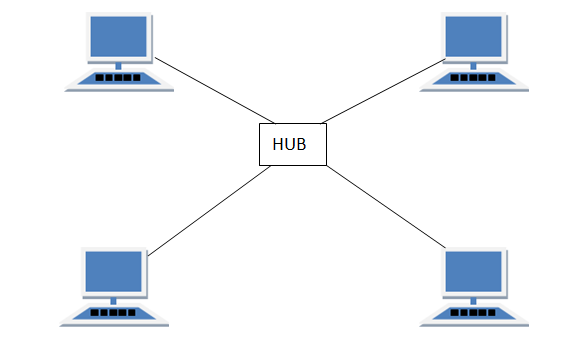
Advantages
- Centralized control of network.
- It is easy to find and correct errors.
- If one computer fails, it will have no effect on other computers on the network.
Disadvantages
- Long cable length
- If the hub fails then the whole network is stopped .
- Wiring closet is required.
iii. Tree Topology
It has a root node and all other nodes are connected to it forming a inverted tree structure. It is actually extended version of bus topology.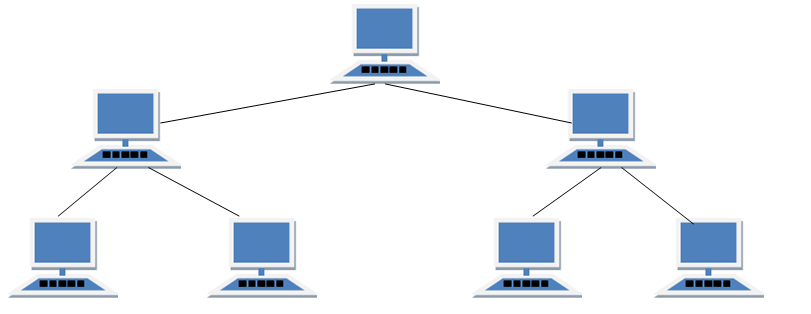
Advantages
- It is easy to add a new node .
- It can be easily managed and maintained.
Disadvantages
- Long cable length.
- It is difficult to locate and correct errors.
Q2. What is TCP/IP?
TCP/IP is a collection of protocols that includes Transmission Control protocol and Internet protocol.
TCP ensures that data reaches its destination succesfully.
IP is meant for establishing connection between two computers on a network.
Q3. What is FTP
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. It is used to transfer files from one computer to another on a network. It is also used to transfer files from a computer to web server.
Q4. What is PPP?
PPP stands for Point – to – Point Protocol. It is a communication protocol used to transmit multiprotocol data between two directly connected (point-to-point) computers.
Q5. What is HTTP?
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It is used to transfer hypertext based documents from one computer to another computer.
Q6. What is SMTP?
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It is used to transfer emails from one computer to another computer.
Q7. What is POP3?
POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol version 3. It is used to receive emails from a remote server to a local email client. It allows to download email messages on local computer and read them even when our computer is offline.
Q8. What is Telnet?
It is also known as Remote Login. It is a tool to access a computer lying at far away place.
Q9. What is GSM?
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communication. It describes the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets.
Q9. What is GPRS?
GPRS stands for General Packet Radio Service. It is a packet oriented mobile data standard on the 2G and 3G mobile communications system.
Q10. What is WLL?
WLL stands for Wireless Local Loop. It is just like a land line phone without wires. It uses radio links to connect to local exchange for connecting to internet and transmission of data. It works in limited geographical area.
Q11. Explain 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G technologies.
1G stands for first generation of mobile technologies. Its speed was upto 2.4 Kbps and it used analog signals.
2G stands for second generation of mobile communication. Its speed was upto 64Kbps. It also allowed text messages and picture messages.
3G stands for third generation of mobile communication. Its speed was upto 2Mbps. It provided high speed internet with support for sending and receiving large e-mails , Video conferencing, 3D games and mobile TV.
4G stands for fourth generation of mobile communication. Its speed was upto 1Gbps. It provided mobile multimedia, global mobility with mobile broadband anywhere.
5G stands for fifth generation of mobile communication. Its has no speed limit. It provides multimedia content of HD quality, better audio/video quality and support for interactive multimedia content.
Q12. What is VOIP?
VOIP stands for Voice Over Internet Protocol. It is a technology that allows to make voice calls using a broadband Internet connection instead of a regular phone line.
Q13. What is WI FI?
Q14. What is WiMax?
WiMax stands for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access. It represents fourth generation of wireless Internet. It allows users to connect to the high speed wireless Internet that can cover very large distance.
Q15. What is VIRUS? What threats are caused virus? How can we prevent virus?
VIRUS stands for Vital Information Under Seize. It is computer software that can harm computer.
Threats caused by VIRUS are:
- Virus may corrupt file system.
- It may format the hard disk.
- Virus can delete file from computer.
- It may eat up entire memory hence crashing the system.
Steps to prevent VIRUS
- Install an updated Anti-Virus Software.
- Regularly scan the computer for virus.
- Don’t download any software from unknown source.
- Don’t use infected pen drive , CD or DVD on computer.
Q16. What is WORM?
WORM is a type of software that can replicate itself creating multiple copies of itself. In this way it may eat up entire disk space hence resulting in system crash.
Q17. What is Trozan Horse?
Trozan Horse is a software that looks legitimate but actually can harm the computer system.. It may appear like a game or similar application.
Q18. What is SPAM?
Spam is an email that you receive from unknown sender. It may contain link to virus or harmful content.
Q19. What is a cookie?
These are the text messages which are sent to a web browser by a web server. Cookies are used to monitor the activities of a user on a web site. These messages are stored as text files on the user’s computer. Cookies don’t harm the computer.
Cookies can contain username and password for a specific website. Many e-commerce websites use cookies to keep track of the items in a user’s shopping cart.
Q20. What is Firewall? How can we provide protection using firewall?
It is a collection or hardware and software which prevent unauthorized access to the network.
Q21. What is HTTPS?
HTTPS stands for Hypertext transfer protocol secure. It is the secure version of HTTP, which is the primary protocol used to send data between a web browser and a website
Q22. What is IT Act?
IT Act( Information Technology Act) came into existence in year 2000. It is the primary law in India to deal with cyber crimes and electronic commerce.
Q23. What is Cyber Law?
All the legal and regulatory aspects related to internet are known as cyber law.
Applications of cyber law:
- To prevent criminal activities on internet.
- To ensure secure transmission of data on internet.
Q24. What is Cyber Crime?
All the illegal activities on intenet are known as cyber crime. Various activities covered under cyber crime are:
- To steal someone’s personal or confidential data.
- To publish offensive content or use abusive language against anyone through internet.
- To break into a secure system.
Q25. What are IPR issues?
IPR stands for Intellectual Property Rights. It is a general term that covers patents, copyrights, trademarks, industrial designs. It ensures that no one can misuse the creative work of someone else.
Q26. What is hacking? Define hacker and cracker.
Hacking refers to activities that seek to compromise digital devices, such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and even entire networks.
Hacker is a programmer who is interested in gaining knowledge about computers and networking.
Cracker is a malicious programmer who breaks into security systems.
Q27. What is WWW?
WWW stands for World Wide web. It is a collection of protocols required for transmitting documents on internet.
Q28. What is HTML?
HTML stands for hypertext markup language. This language is used to create web pages. HTML is used to format a web page. It is used to create a static web page.
Q29. What is XML?
XML stands for Extensible Markup Language. It is used to creating documents which can contain structured information.
Q30 What is Domain Name?
Domain name specifies the type of a web site. Domain names are categorized into two types:
As per use:
| .com | Commercial |
| .org | Organizational |
| .net | Network based |
| .gov | Governmental |
As per country
| .in | India |
| .uk | United Kingdom |
| .us | United States |
Q31. What is URL (Uniform Resource Locator)?
URL is the complete name of a document on a website. It includes the protocol being used, the address of the web site where the document is located, the sub-directory and name of the file.
A URL has three parts
- Protocol
- Domain name server where the page is located
- the filename for the page
E.g. http://www.yahoo.com/index.html
http is the protocol, www.yahoo.com is the domain name server, index.html is the filename of a file on the server
Q32. What is a Web site?
It is defined as a collection of web pages.. A document which supports hypertext is known as a web page.
Q33. What is a Web Browser?
It is a software used to display web pages and web sites. The important web browsers are
- Microsoft Internet Explorer
- Mozilla Firefox
- Google Chrome
Q34. What is Web Server?
Web Server is a computer that stores web server software and a website’s component files.
Q35. What is Web hosting?
It is the process in which a web site is stored on a computer in such a way so that it should be accessible by other computers through internet.
Q36. What is web scripting? What are its types?
Web Scripting is the way to make web pages dynamic. Scripting is of two types
- Client Side Scripting
- Server Side Scripting
i. Client Side Scripting: In this case, scripting works at the client’s browser.
Example: Javascript, VBScript.
ii. Server Side Scripting: In this case, scripting works at the Server.
Example:
a. JSP(Java Server Pages): It is java based technology to create dynamic web pages.
b. PHP(Hypertext Preprocessor): It is open source scripting language to create dynamic web pages.
c. ASP(Active Server Pages): It is product of microsoft to create dynamic web pages. ASP pages can run only windows based computers.
Q37. What is Web 2.0? What are its impacts on social networking?
Web 2.0 means those internet applications which allow sharing and collaboration opportunities to people and help them to express themselves online.
It has greatly impacted social networking websites and applications where people can easily share content supporting participatory culture and interoperability.
Web 2.0 examples include Video sharing sites (YouTube), social networking (Facebook), Microblogging (Twitter), Instagram etc.
Q38. What is E-Commerce?
E-commerce refers to Electronic commerce in which people can sale and purchase goods online through websites. Payments can be made through online banking, mobile banking and payment apps.
Q39. What is Online banking?
It is also known as Internet banking. It is an electronic payment system that enables customers of a bank to conduct financial transactions through bank’s website.These transactions include sending money, receiving money and checking account balance etc.
Q40. What is Mobile Banking?
It is a service provided by a bank that allows its customers to conduct financial transactions using a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet. These transactions include sending money, receiving money and checking account balance etc.
Q41. What are different Payment apps and services?
There are different payment apps and services available in market. They are;
i. Paypal: It is very popular application using which you can make payment for goods, services as well as international transactions. It has helped many shops to go online. It provides its wallet that can be linked to your bank account.
ii. Google Pay: Google Pay is a mobile payment app that does not have a wallet facility. It allows you to make bank to bank transfers for free.
iii.Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM): It is a payment app that lets you make simple, easy and quick transactions using Unified Payments Interface (UPI). You can make direct bank payments to anyone using their UPI ID or scanning their QR with the BHIM app. You can also request money through the app from a UPI ID.