COMPUTER NETWORKING NOTES FOR CLASS XII – I
Computer networking Notes for class 12- II
Q1. Define a Computer network?
A computer network is an interconnected collection of autonomous computers and devices to exchange information or share resources.
Q2. Explain different components of a computer Network.
1. Host /Node / Workstation
Host or node or workstation refers to the computers that are attached to a network.
2. Server
Computer that facilities sharing of data ,software ,and hardware resources (e.g. printers, modems etc.) on a network is called server.
3. Client
A client computer is a computer that can request for some services from a server.
4. NIU (Network Interface Unit)
NIU is also known as NIC(Network Interface Card) or LAN Card. It is a device that works as an intermediator between computer and the network.
LAN Card can be wired as well as wireless.
5. Hub/switch
Hub/ Switch is a device used to interconnect computers on a network.
6. Communication channel
Communication channel is way/method to provide communication between computers and devices on a network. .Communication channel is of two types:
a. Wired Communication channels
Wired communication channels include cables to interconnect computers on a network. There are basically three types of wired communication channels:
i. Twisted pair cable
ii. Coaxial cable
iii. Optical fiber cable.
b. Wireless Communication channel
Wireless communication channels include wireless methods to interconnect computers on a network. Various types of wireless communication channels are:
i. Radio waves
ii. Satellite
iii. Microwave
iv. Infrared waves
v. Laser
7. Software
Communication is not possible on a network without software components. Different software components include network protocols ,network operating system etc.
8. Network Services
They refef to the applications that provide different functionalities over a network. They include DNS(Domain Name System), file sharing ,VoIP(voice over IP) etc.
Q3. What are advantages of a Computer Network
1. Resource sharing : We can share hardware devices, softwares as well as data on a network.
2. Communication Medium : Network can provide communication between different computers attached to a network.
3. Reduced Cost : Sharing of resources helps in reducing hardware and software cost
4. Centralized Control: We can centrally control the computers attached to a network.
5. Central storage of data: We can save data of entire network on single computer. It helps in removing duplication of data as well as maintaining integrity of data.
Q4. What is ARPANET?
ARPANET stands for Advanced Research Project Agency Network. It was the first network developed by DOD (Department of Defence) America).
Q5. Explain different types of computer Networks ?
| LAN | MAN | WAN | PAN |
| 1. It stands for Local Area Network | 1. It stands for Metropolitan Area Network | 1. It stands for Wide Area Network | 1. It stands for Personal Area Network |
| 2. It is a network within a small area such as building. | 2. It is a network within a city. | 2. It is a network across cities, countries and continents. | 2. It is a network within a very small area upto 10 meters. |
| 3. Twisted pair cable is preferably used for communication. | 3. Coaxial cable is preferably used for communication.. | 3. Optical fiber or satellite are used for communication | 3. Communication is made using bluetooth, infrared or wireless devices. |
| 4. Example: Computer Lab | 4. Example: Cable TV Network | 4. Example: Mobile phone network | 4. Example: Wireless headphone, wireless printer. |
Q6. What is Communication channel?
Communication channel is way/method to provide communication between computers and devices on a network.
Q7. What are types of Communication channel?
Communication channel is of two types:
- Wired communication channel
- Wireless communication channel
a. Wired Communication channels
Wired communication channels include cables to interconnect computers on a network. There are basically three types of wired communication channels:
i. Twisted pair cable
A twisted pair cable is a collection of four pair of insulated wires wrapped together. They are preferably used for local area network.
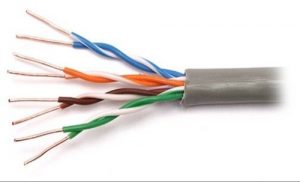
Advantages
- They are very cheap.
- They have very less weight.
- They are flexible.
- It is easy to install and maintain twisted pair cable.
Disadvantages
- It is suitable for short distance communication.
- It has low bandwidth.
They are available in various forms such as CAT1,CAT2 CAT3,CAT4,CAT5,CAT6.
They are basically of two types
a. Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
b. Unshielded Twisted Pair(UTP)
ii. Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable consists of a solid wire surrounded and insulator further surrounded by wire mesh further covered with plastic insulator.

Advantages
- It is suitable for cable TV transmission.
- It provides high bandwidth so it suitable for long distance communication.
- It is suitable for broadband transmission.
Disadvantages
- It is more expensive compared to twisted pair cable.
- It is less flexible.
- It is not compatible with twisted pair cable.
They are of two categories: Thicknet and Thinnet.
iii. Optical fiber cable
Optical fiber cable is make of glass or glass like material. It can transmit information in the form of light waves. Optical fiber consists of following parts:
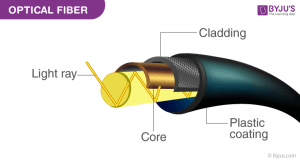
- Core: It is the material at the center of optical fiber cable to transmit light waves.
- Cladding: It is covering of core used to reflect the light back to the core.
- Plastic Coating: It is the plastic coating to protect cable from damage.
Advantages
- It is free from electromagnetic interference.
- It provides high for long distance communication.
Disadvantages
- It is very expensive.
- It is difficult to join these cables..
- It is not compatible with other cables.
There are two categories of Optical fiber cable
i. Single node
ii. Multi –node .
b. Wireless Communication channel
Wireless communication channels are used to transmit information without using cables.Various types of wireless communication channels are:
- Radio waves
- Microwave
- Satellite
- Infrared Waves
- Laser
- Bluetooth
- Wi-Fi
i. Radio waves
Radio waves communication uses continuous sine waves to transmit information from one point to another. It needs two components:
a. Transmitter: To transmit information.
b. Receiver: To receive information transmitted by transmitter.
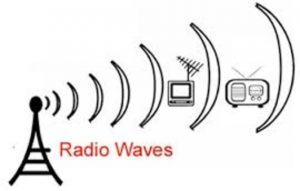
Advantages
- It is easy to install and maintain.
- It is suitable for hilly areas as well as oceans.
Disadvantages
- It is insecure.
- It is badly affected by weather.
ii. Microwave
Microwave is direct line of sight transmission in which parabolic antennas are placed in front of each other.

Advantages
- It is cheap way of communication
- It is suitable for hilly areas as well as oceans.
Disadvantages
- It is insecure.
- It is badly affected by weather.
iii. Satellite
In satellite communication, artificial satellite is placed in geostationary orbit at around 36,000 Kms above the surface of earth.
A satellite contains Trans-Receiver antenna to receive, generate and redirect signals.
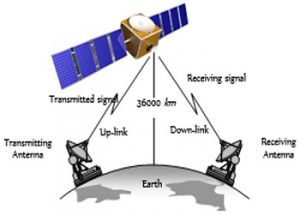
Advantages
- It covers a very large area.
- It provides secure transmission.
Disadvantages
- It is very expensive.
- Installation is very complex.
iv. Infrared Waves
Infrared is direct line of sight transmission within a short distance (5 meters).
Advantages
- It is cheap way of communication
Disadvantages
- It can’t cross walls and solid objects.
- It is not suitable for long distance communication.
v. Laser
Laser is direct line of sight transmission .
Advantages
- It is cheap way of communication
- It is suitable for short range transmission of signals like TV remotes, wireless speakers.
Disadvantages
- It can’t cross walls and solid objects.
- It is badly affected by weather.
Q8. What is bandwidth?
Bandwidth is defined as amount of information that can be transferred through a single channel per unit time.
It is also defined as difference between highest and lowest frequencies of a transmission channel.
For analog channels, bandwidth is measured as Hz (Hertz), KHz (Kilo Hertz) ,MHz(Mega Hertz)
For digital channels, bandwidth (Data transfer Rate) is measured as bps (Bits per second), Kbps (Kilo Bits per second) , Mbps(Mega Bits per second), Gbps(Giga Bits per second), Tbps(Tera Bits per second).
Q9. What is Internet?
Internet stands for interconnected networks. It is interconnection of computers all over the world.
Q10. What is Interspace?
Interspace is basically a client/server software program that allows multiple users to communicate online with real-time audio, video or text chat in dynamic 3D environments.
Q11. What is MAC Address (Media Access Control Address)?
MAC address refers to the physical address assigned by NIC manufacturer. MAC address is a 6-byte address with each byte separated by a colon
Example: 10: B5:03:63:2E: FC
First 3 bytes are Manufacturer id (10:B5:03)
Last 3 bytes are Card Number (63:2E:FC)
Q12. What is switching and its types?
Switching is the technique of transmitting information from one device/network to another.
There are three types of switching.
i. Circuit Switching: In packet switching, a physical communication link is established between source and destination computer/device before transmitting information.
ii. Message Switching: In message switching, information is transferred from source computer to first switching office, then a communication path is established with another switching office. From there it is transferred to destination computer.
iii. Packet Switching: In packet switching, information is transferred from source computer to destination computer in the form of fixed sized blocks known as packets.
Q13. What is MODEM?
MODEM stands for Modulator/Demodulator. It is device used to convert analog signal to digital signal and vice versa. It is basically used to run internet on your computer/device.
Q14. What is RJ45?
RJ45 stands for Registered Jack 45. It is an 8 wire connector used to connect computers on a. LAN or Ethernet Card.
Q15. What is Ethernet Card?
Ethernet Card is also known as LAN Card. It is used to attach a computer on a network.
Ethernet Card is the first LAN card developed by XEROX corporation along with INTEL and DEC (Digital Equipments Corporation).
Q16. What is a Hub?
 Hub is a device having multiple ports used for interconnecting multiple computers together.
Hub is a device having multiple ports used for interconnecting multiple computers together.
Hub provides shared bandwidth to all connected computers.
Hubs are of two types.
i. Active hub : It amplify the signal when it moves from one computer to another.
ii. Passive hub: It allows the signal to pass from one computer to another without any change.
Q17. What is a Switch
A switch is a device used to interconnect computers on a network but it provides dedicated bandwidth to all connected computers.
Q18. What is a Bridge?
A bridge is a network device used to interconnect two networks that follow same protocols.
Q19. What is a Router?
A router is a network device used to interconnect networks having different protocols. Router forwards data from one computer to another by shortest path.
Q20. What is a Gateway?
A gateway is a network device used to interconnect dissimilar networks. It establishes an intelligent connection between local networks with completely different structures.
Q21. What is WiFi Card?
A WiFi card is an internal or external Local area network adapter with a builtin wireless radio and antenna.
Q22. What is a repeater?
Repeater is a network device used to amplify week signal. Signal gets week over long distance so we need a repeater to restrengthen it.